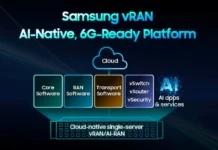
According to the IDC, approximately 12.4% of respondents from telecom operators in the Asia/Pacific region view the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) as a significant factor in the implementation of 5G services. In line with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, IDC emphasizes that sustainability is a crucial business strategy for the future.
This strategy supports initiatives such as smart manufacturing, energy-efficient construction, and eco-friendly industrialization. Industry 4.0 combines traditional manufacturing processes with digital technology, AI, and IoT to address these goals. IDC forecasts significant growth in 5G connections, including mobile subscribers and IoT connections, in the Asia/Pacific region, with the number of connections projected to increase from 574 million in 2021 to 3,234 million by 2025, representing a five-year CAGR of 87.9%.
IDC highlighted that telecommunications companies primarily view key industries such as manufacturing, smart cities with smart mobility, and smart buildings as the most crucial areas where 5G implementation will have a significant impact.
By embracing digitization and connectivity, organizations can facilitate the transition to a greener and more sustainable future. One of the key principles of Industry 4.0 is that efficiency leads to energy savings, implying that any energy-saving measures taken by organizations ultimately enhance efficiency. Throughout the Asia/Pacific region, manufacturing facilities have already adopted private or dedicated networks to control various on-site equipment.
As per IDC, unstable wireless communication and latency are the primary obstacles hindering the adoption of digital transformation in businesses. These challenges can be overcome through the deployment of fifth-generation (5G) networks, which offer more reliable communication. Additionally, private 5G networks can ensure dependable connectivity for IoT devices.
The findings indicate that digital technologies, including 5G, IoT, AI, machine learning (ML), and smart building solutions, can significantly reduce emissions in smart factories. This reduction is achieved through faster and more efficient production lines, as well as increased energy. efficiency.