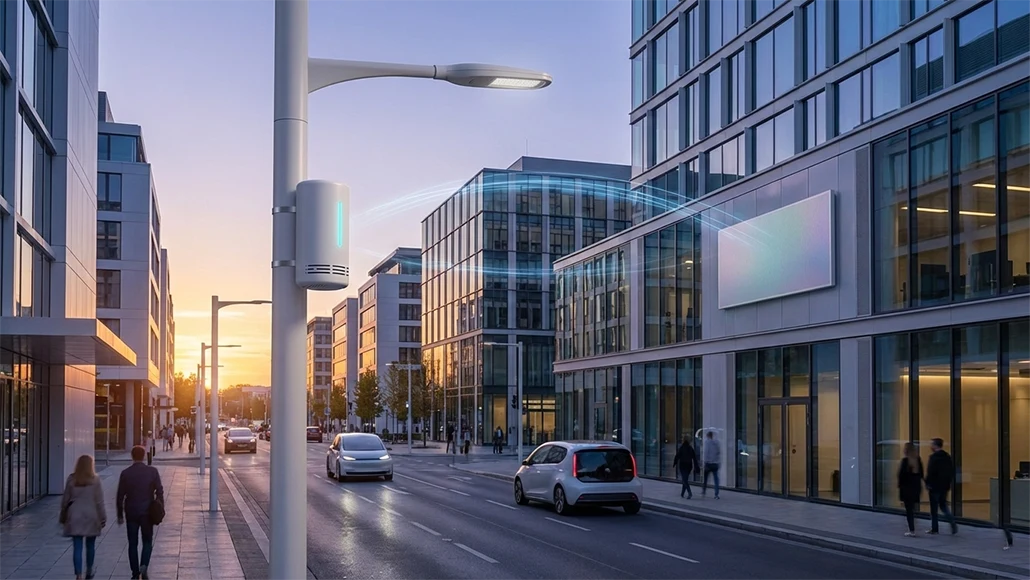
The world of telecommunications has always been defined by a series of generational leaps, each bringing a new dimension to human interaction. From the basic voice calls of 1G to the mobile internet of 3G and the high-speed streaming of 4G and 5G, each step has expanded the boundaries of our digital lives. However, the move toward 6G innovation future telecom networks is fundamentally different. While previous generations focused primarily on increasing the speed and volume of data transmission, 6G is being designed as a comprehensive platform for the “Internet of Senses” and the “Internet of Intelligence.” This new era of connectivity will not just move data; it will move consciousness, allowing for a level of immersion and environmental awareness that will redefine the human experience in ways we are only beginning to comprehend.
The Architecture of AI Native Networks and Autonomous Connectivity
A primary differentiator of the sixth generation of wireless technology is the shift toward AI native networks. In the 5G era, artificial intelligence is an external tool used to optimize specific network functions. In the 6G world, intelligence is the very foundation of the architecture. Every node, switch, and transmitter in a 6G environment will possess inherent machine learning capabilities. This allows the network to be entirely self-organizing and self-optimizing. It can predict user movement, anticipate data surges, and even reconfigure its own physical parameters to ensure that every user receives a consistent, high-quality connection regardless of their location. This level of advanced connectivity is essential for the next wave of industrial automation, where millions of sensors and robots must communicate with zero latency and absolute reliability.
Exploring the Terahertz Frontier and Spectrum Management
To achieve the staggering data rates promised by 6G with targets as high as 1 Terabit per second the industry is looking toward the Terahertz (THz) spectrum. This high-frequency range offers vast amounts of bandwidth but comes with significant physical challenges. THz waves have a very short range and are easily blocked by objects as simple as a human hand or a raindrop. Overcoming these hurdles requires revolutionary spectrum management and antenna design. 6G innovation future telecom networks will likely utilize “intelligent reflecting surfaces” materials that can be applied to buildings and walls to steer signals around obstacles. By turning the physical environment itself into part of the network, engineers can ensure that high-frequency signals reach their destination with minimal loss, providing the “omnipresent” coverage that 6G demands.
The Evolution of Telecom Infrastructure and Edge Computing
The physical manifestation of 6G technology will differ significantly from the cell towers we see today. The future will be defined by a massive densification of the network, with small cells integrated into everything from street lamps to domestic appliances. This distributed telecom infrastructure will also serve as a decentralized computing platform. By moving processing power to the extreme edge of the network, 6G eliminates the delay caused by sending data to distant data centers. This is the key to achieving the sub-millisecond latency required for holographic telepresence where high-resolution 3D images of people appear to be physically present in a room and for the real-time coordination of thousands of autonomous vehicles in a complex urban environment.
Wireless Innovation and the Convergence of Sensing and Communication
One of the most profound aspects of 6G innovation future telecom networks is the concept of “joint communication and sensing.” In this model, the wireless signals used for data transmission also act as a high-resolution radar system. The network itself becomes aware of the physical objects within its coverage area, mapping the environment in three dimensions with incredible precision. This allows the network to “see” without the need for cameras, identifying a person falling in a smart home or a vehicle approaching a blind corner. This synergy between communication and environmental awareness will drive a new generation of healthcare and safety applications, where the connectivity infrastructure itself acts as a silent guardian, monitoring our well-being and protecting us from harm.
Global Standards and the Geopolitics of Next Generation Telecom
The journey toward 6G is not just a technical challenge; it is a complex geopolitical and regulatory endeavor. Establishing a single global standard for 6G is essential to ensure that a device purchased in Tokyo works seamlessly in New York or London. However, as telecommunications becomes a core component of national security and economic sovereignty, the competition to define these standards has intensified. International cooperation is required to manage spectrum allocation and to ensure that the benefits of 6G technology are shared across the globe, preventing a “digital divide” that could leave developing nations behind. The policy decisions made in the next few years will shape the digital landscape for the remainder of the century, determining how we connect, trade, and govern in a hyperconnected world.
Security by Design and the Post-Quantum Challenge
As we entrust more of our personal and professional lives to the network, the importance of security becomes existential. 6G innovation future telecom networks must be built with a “security by design” philosophy that addresses both current and future threats. With the potential arrival of quantum computing, traditional encryption methods may soon become obsolete. Therefore, 6G researchers are exploring “quantum-resistant” cryptography and physical layer security to ensure that data remains private even in the face of unprecedented computational power. In a world where the network is aware of our physical location and even our physiological state, protecting the privacy and integrity of this data is the most critical challenge facing the telecommunications industry.
The Internet of Senses and the Future of Human Interaction
Looking ahead, 6G will enable the “Internet of Senses,” where high-fidelity haptic feedback, smell, and even taste can be transmitted digitally. This will revolutionize everything from remote education to the way we shop. Imagine being able to “feel” the fabric of a garment before buying it online, or a surgeon being able to “sense” the resistance of tissue while performing an operation on a different continent. This level of immersion will blur the lines between physical and digital presence, allowing us to be “anywhere” at “any time.” While the social and psychological implications of this shift are profound, the potential to bring the world closer together and to solve complex problems through remote collaboration is limitless.
Sustainable Connectivity and the Green 6G Movement
Finally, the development of 6G must be balanced with the urgent need for environmental sustainability. A network of billions of devices could potentially consume a staggering amount of energy. To prevent this, the “Green 6G” movement is focusing on ultra-low-power hardware and AI-driven energy management. By using machine learning to power down network components when they are not in use and by exploring energy-harvesting technologies that allow sensors to run without batteries, 6G can become the most energy-efficient generation of wireless technology yet. This commitment to sustainability ensures that the future of telecom networks is not only faster and smarter but also compatible with the long-term health of our planet.
Key Takeaways:
- 6G is an AI-native architecture that integrates intelligence at every level to create a self-healing, self-optimizing global network.
- The use of the Terahertz spectrum and intelligent reflecting surfaces will provide the bandwidth and omnipresence required for holographic communication and the Internet of Senses.
- The convergence of sensing and communication allows the network to map the physical world in real-time, enabling revolutionary safety, health, and industrial applications.