Sustainable Telecom Networks
The telecommunications industry stands at a critical juncture where environmental responsibility and business sustainability converge to drive fundamental transformation in network operations and infrastructure development. As the sector contributes up to 2% of global carbon emissions while networks account for over 75% of telcos’ total energy consumption, operators worldwide are implementing comprehensive sustainability strategies that encompass renewable energy adoption, energy efficiency optimization, and innovative green technologies. This transformation represents more than environmental compliance; it embodies a strategic imperative that influences customer relationships, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational viability.
The Sustainability Challenge
Telecommunications networks, encompassing both mobile and fixed infrastructure, represent the largest energy consumption component for operators globally. The expansion of digital connectivity drives increasing energy demands as 5G deployment, fiber network construction, and data center operations require substantial power resources to maintain continuous operation.
The industry’s environmental impact extends beyond direct energy consumption to include equipment manufacturing, transportation, and end-of-life disposal considerations. Comprehensive sustainability approaches must address the entire telecommunications value chain while maintaining service quality and supporting continued digital transformation.
Energy Transition Strategies
Renewable Energy Adoption
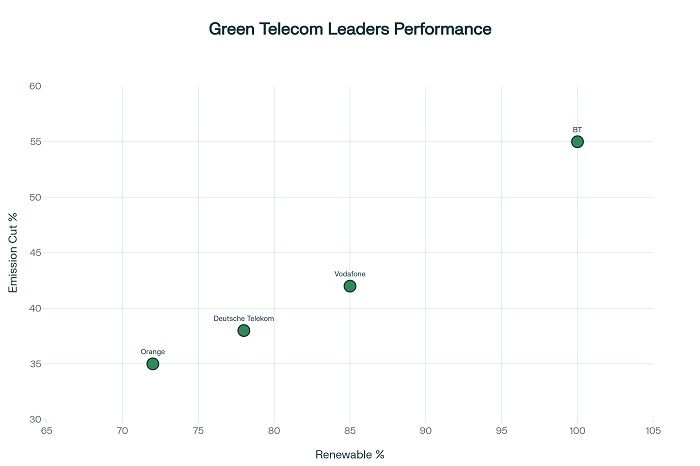
Leading telecommunications companies have achieved remarkable success through aggressive renewable energy adoption programs that demonstrate both environmental and economic benefits. BT’s sustainability journey exemplifies comprehensive transformation, achieving 100% renewable electricity consumption in 2020 while reducing Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 55%.
The business case for renewable energy extends beyond environmental benefits to include substantial cost savings and operational advantages. BT’s early sustainability initiatives resulted in savings of approximately 220 million pounds while supporting accelerated decarbonization timelines that advance net-zero targets by 14 years.
Grid Integration and Smart Energy Management
Telecommunications infrastructure plays an essential role in enabling renewable energy integration through advanced communication systems that monitor and control decentralized energy resources. This dual function positions telcos as both consumers and enablers of sustainable energy systems.
Smart energy management systems leverage telecommunications networks to optimize renewable energy distribution while reducing waste and improving grid stability. This integration creates synergies between telecommunications and energy infrastructure that support broader sustainability objectives.
Operational Efficiency Optimization
Network Modernization
Fiber network deployment delivers significant energy efficiency advantages compared to legacy copper infrastructure, with fiber networks consuming 70 to 80 percent less energy per connection. This efficiency gap continues expanding as more energy-efficient fiber technologies emerge, making copper network decommissioning critical for sustainability goals.
Comprehensive copper migration requires both fiber availability and commercial campaigns to persuade customers to upgrade services. The scope of decommissioning benefits depends on implementation scale, with complete network cluster migration enabling parallel infrastructure elimination and maximum efficiency gains.
Artificial Intelligence for Energy Optimization
AI emerges as one of the most powerful tools for reducing telecommunications carbon footprints through intelligent network optimization and predictive maintenance. Leading companies including Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom, and Ericsson leverage AI for anomaly detection, interference source identification, and equipment issue prediction.
Vodafone’s AI implementation enables real-time network optimization while detecting potential problems before they impact service quality. This approach reduces energy consumption while improving network reliability and customer satisfaction through proactive maintenance strategies.
Infrastructure Sharing and Efficiency
Radio Access Network sharing enables multiple operators to reduce energy consumption through consolidated infrastructure deployment. In Poland, Orange and T-Mobile achieved 20% site number reduction through RAN sharing, resulting in energy consumption savings of up to 30% per site.
Infrastructure sharing reduces redundant network deployment while maintaining competitive service delivery. This collaborative approach enables industry-wide efficiency improvements while reducing individual operator infrastructure investment requirements.
Technology Innovation for Sustainability
Virtual Power Plant Development
Progressive operators leverage telecommunications infrastructure for virtual power plant creation that contributes to renewable energy system stability. Elisa’s conversion of lithium-ion battery capacity into a virtual power plant demonstrates innovative approaches to energy optimization and revenue generation.
The virtual power plant stores energy from renewable sources and releases it during high-demand periods while providing grid stability services. This approach offers operational advantages including extended backup capacity and additional income from energy sales to support green energy investment business cases.
Equipment Lifecycle Management
Sustainable equipment lifecycle management encompasses procurement, deployment, operation, and disposal considerations that minimize environmental impact. This comprehensive approach requires supplier collaboration and circular economy principles that extend equipment useful life while reducing waste.
Innovative approaches include equipment refurbishment programs, component recycling initiatives, and design for sustainability requirements that influence supplier selection and network architecture decisions. These programs reduce environmental impact while often providing cost advantages through extended equipment utilization.
Regional Sustainability Leadership
European Telecommunications Initiative
European telecommunications operators demonstrate industry leadership through aggressive net-zero commitments that target 2030 for Scope 1 and 2 emissions and 2040 for Scope 3 emissions. The European Telecommunications Network Operators’ Association coordinates industry efforts while supporting regulatory compliance and best practice sharing.
This regional leadership creates competitive advantages for European operators while establishing standards that influence global industry practices. The comprehensive approach encompasses direct operations and supply chain emissions reduction to address the majority of telecommunications environmental impact.
Asia-Pacific Innovation
Asia-Pacific telecommunications companies increasingly integrate sustainability considerations into network deployment and operational strategies. This includes renewable energy procurement, energy-efficient technology adoption, and innovative applications of telecommunications infrastructure for environmental monitoring.
The region’s rapid digital growth creates opportunities for sustainable technology deployment from the initial network design phase. This approach enables more comprehensive sustainability integration compared to retrofitting existing infrastructure with efficiency improvements.
Economic and Business Benefits
Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency
Renewable energy adoption and energy efficiency improvements deliver substantial cost reductions that justify sustainability investments. McKinsey research demonstrates that companies can achieve 15 to 30 percent energy cost savings through holistic approaches combining technology improvements with operational optimization.
These cost savings support business case development for continued sustainability investment while providing competitive advantages through reduced operational expenses. The financial benefits create positive feedback loops that accelerate sustainability program expansion and improvement.
Customer and Stakeholder Value
Sustainability initiatives enhance brand value and customer relationships as consumers increasingly prioritize environmental responsibility in supplier selection. This customer preference creates market opportunities for operators with strong sustainability credentials while supporting premium pricing for green services.
Investment community focus on environmental, social, and governance criteria influences capital access and cost while creating accountability for sustainability performance. This external pressure supports continued investment in green technologies and operational improvements.
Supply Chain Sustainability
Supplier Engagement and Requirements
Comprehensive sustainability strategies extend beyond direct operations to encompass supply chain emissions that often represent the majority of telecommunications environmental impact[26]. BT’s supplier engagement program targets 42% reduction in Scope 3 emissions by 2030 through new requirements for supplier emissions reduction and renewable energy procurement.
This supply chain focus creates cascading positive impacts as telecommunications companies drive suppliers toward low-carbon operations. The approach leverages telecommunications purchasing power to accelerate broader industry transformation while addressing comprehensive environmental impact.
Green Bond Financing
Many telecommunications operators issue green bonds to finance sustainability investments including energy efficiency improvements, renewable energy deployment, and network modernization projects. Companies including Vodafone, KPN, Proximus, Telefonica, and Orange have issued green bonds to support sustainability initiatives.
Green bond financing demonstrates investor confidence in telecommunications sustainability strategies while providing dedicated funding for environmental improvement projects. This financing approach enables accelerated sustainability investment while maintaining financial flexibility for other business requirements.
Future Development Trajectory
Next-Generation Network Sustainability
6G network development provides opportunities for comprehensive sustainability integration from initial design phases. This includes energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy integration, and circular economy principles that minimize environmental impact throughout network lifecycles.
Future networks will increasingly integrate sustainability considerations as core design requirements rather than secondary optimization opportunities. This approach enables more comprehensive environmental performance while supporting regulatory compliance and stakeholder expectations.
Technology Convergence for Sustainability
The convergence of telecommunications, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy technologies creates new opportunities for integrated sustainability solutions. These technologies enable more sophisticated optimization while supporting broader environmental objectives across multiple industries.
Continued innovation in sustainable telecommunications technologies will drive industry transformation while creating competitive advantages for early adopters. This technology development supports both environmental objectives and business performance through improved operational efficiency and customer value creation.
The telecommunications industry’s sustainability transformation represents a fundamental shift that addresses environmental responsibility while creating business value through operational efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced stakeholder relationships. Success requires comprehensive strategies that encompass direct operations, supply chain engagement, and innovative technology adoption. Operators that embrace sustainability leadership position themselves advantageously for long-term success in an increasingly environmentally conscious market while contributing to global climate objectives and sustainable development goals.