The telecommunications and cloud computing industries are experiencing unprecedented convergence as operators and hyperscale cloud providers simultaneously compete and collaborate in the rapidly evolving digital infrastructure landscape. This convergence transforms traditional industry boundaries while creating new opportunities for innovation, service delivery, and revenue generation. The integration of telecom networks with cloud technologies, particularly through edge computing and 5G deployment, establishes the foundation for next-generation digital services that require seamless connectivity and computing capabilities.
The Convergence Imperative
Telecommunications operators and cloud service providers face mounting pressure to deliver integrated solutions that combine connectivity, computing, and storage capabilities[. This integration becomes essential as enterprise customers demand comprehensive digital infrastructure solutions rather than separate connectivity and computing services.
The convergence acceleration reflects the increasing importance of low-latency applications, real-time data processing, and distributed computing architectures. These requirements cannot be satisfied through traditional centralized cloud models alone, necessitating the integration of network and computing resources at the edge.
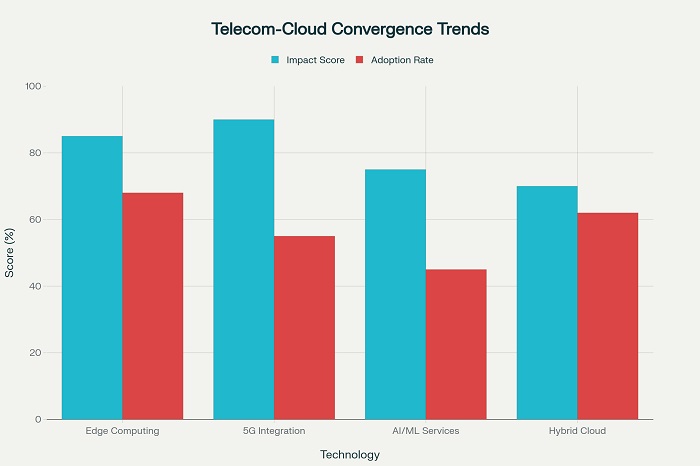
Edge Computing as the Catalyst
Distributed Computing Architecture
Edge computing represents the primary driver of telecom-cloud convergence by bringing computing resources closer to data sources and end users. This distributed approach reduces latency, enhances real-time decision-making capabilities, and minimizes bandwidth usage compared to centralized cloud architectures.
Telecommunications providers leverage their network infrastructure to deploy edge computing capabilities at base stations, central offices, and network aggregation points. This infrastructure advantage positions telcos competitively against traditional cloud providers in latency-sensitive applications.
5G and Edge Integration
The combination of 5G networks and edge computing creates powerful synergies that enable ultra-low latency applications including autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality. 5G’s high-speed, low-latency capabilities provide the connectivity foundation while edge computing delivers the processing power required for real-time applications.
This integration enables telecommunications operators to participate in the broader cloud computing market while leveraging their unique network assets. The result is a more comprehensive value proposition that addresses both connectivity and computing requirements.
Competitive Dynamics and Collaboration
Hyperscaler Partnerships
Major cloud providers including Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud increasingly partner with telecommunications operators to extend their services to network edges. These partnerships combine cloud platforms with telco infrastructure to create distributed computing solutions that neither party could deliver independently.
Collaboration models vary from infrastructure sharing arrangements to joint service development initiatives. These partnerships enable cloud providers to access telco infrastructure while allowing operators to participate in the growing cloud services market.
Competitive Tensions
Despite collaboration opportunities, fundamental tensions exist between telecommunications operators and cloud providers as they compete for enterprise customers and infrastructure investment. Cloud providers seek to bypass traditional telecom services through direct connectivity solutions while telcos aim to capture more value from digital transformation initiatives.
The competitive landscape becomes increasingly complex as both industries expand into adjacent markets while maintaining their core business focus. Success requires careful navigation of partnership opportunities and competitive threats.
Network Function Virtualization
Software-Defined Infrastructure
Network Function Virtualization enables telecommunications operators to implement network functions using software running on standard computing hardware rather than dedicated appliances. This approach increases flexibility while reducing costs and enabling rapid service deployment.
Virtualization technologies allow telcos to implement cloud-like operational models within their network infrastructure. This transformation enables operators to deliver network services with the agility and scalability associated with cloud computing platforms.
Cloud-Native Network Functions
The evolution toward cloud-native network functions enables telecommunications operators to leverage container technologies, microservices architectures, and DevOps methodologies. These approaches improve operational efficiency while enabling rapid innovation and service development.
Cloud-native implementations position telcos to integrate more effectively with hyperscale cloud platforms while maintaining operational control over network functions. This architecture supports hybrid deployment models that combine on-premises and cloud resources.
Industry-Specific Applications
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
The convergence of telecom and cloud technologies enables comprehensive Industry 4.0 solutions that combine connectivity, computing, and analytics capabilities. Manufacturing companies leverage these integrated platforms to implement advanced automation, predictive maintenance, and quality control systems.
Private 5G networks combined with edge computing create the foundation for smart manufacturing initiatives that require guaranteed performance and local data processing. This integration enables real-time optimization while maintaining data security and operational control.
Smart Cities and Public Services
Smart city implementations benefit from telecom-cloud convergence through comprehensive sensor networks, data analytics platforms, and citizen service delivery systems. The combination of ubiquitous connectivity and distributed computing enables real-time city management and service optimization.
Edge computing integration ensures that critical city functions can operate independently while benefiting from cloud-scale analytics and optimization. This architecture provides resilience while enabling innovation in public service delivery.
Technology Integration Strategies
API-Driven Service Development
Application Programming Interfaces enable seamless integration between telecommunications and cloud services while facilitating third-party innovation. Telstra and Ericsson’s programmable 5G network demonstrates how APIs can unlock network capabilities for external developers.
API availability enables telecommunications operators to participate in broader digital ecosystems while generating revenue from previously unutilized network capabilities. This approach fosters innovation while maintaining operator control over critical infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI and machine learning technologies benefit from the convergence of telecom and cloud platforms through access to diverse data sources and distributed computing resources. This integration enables more sophisticated analytics and optimization across network and cloud operations.
AI-driven automation becomes possible when telecommunications and cloud platforms share data and processing capabilities. This convergence enables predictive maintenance, automatic optimization, and intelligent resource allocation across integrated infrastructure.
Deployment Models and Architectures
Hybrid Cloud Integration
Hybrid deployment models combine public cloud resources with private infrastructure to optimize performance, security, and cost. Telecommunications operators implement hybrid solutions that leverage both their own infrastructure and hyperscale cloud platforms.
This approach enables operators to maintain control over critical functions while accessing cloud-scale resources for variable workloads. The hybrid model provides flexibility while optimizing resource utilization and operational efficiency.
Multi-Cloud Strategies
Multi-cloud approaches enable organizations to leverage multiple cloud providers while avoiding vendor lock-in. Telecommunications operators increasingly adopt multi-cloud strategies to optimize service delivery and maintain competitive positioning.
The multi-cloud approach requires sophisticated orchestration capabilities to manage resources across different platforms. This complexity creates opportunities for operators to provide integration and management services that add value for enterprise customers.
Economic Implications and Business Models
Revenue Stream Diversification
Telecom-cloud convergence enables operators to diversify revenue streams beyond traditional connectivity services. Edge computing, cloud services, and platform offerings create new monetization opportunities while strengthening customer relationships.
The convergence allows telecommunications operators to capture more value from enterprise digital transformation initiatives. This participation in the broader technology value chain supports sustainable revenue growth and competitive differentiation.
Investment and Infrastructure Sharing
Convergence initiatives require substantial infrastructure investment that can be optimized through strategic partnerships and resource sharing. Collaborative approaches enable both telecommunications and cloud providers to expand capabilities while managing capital requirements.
Infrastructure sharing arrangements reduce redundant investment while accelerating service deployment. These partnerships enable more efficient capital allocation while supporting faster innovation and market expansion.
Future Development Trajectory
6G Preparation
The convergence of telecom and cloud technologies establishes the foundation for 6G network development and deployment. Future networks will integrate computing capabilities more deeply while supporting even more demanding applications and use cases.
6G development requires continued collaboration between telecommunications and cloud industries to create integrated platforms that support advanced applications. This collaboration becomes essential for realizing the full potential of next-generation networks.
Ecosystem Evolution
The ongoing convergence will reshape the broader technology ecosystem as telecommunications and cloud capabilities become increasingly integrated. This evolution creates new competitive dynamics while enabling innovative service delivery models.
Success in the converged environment requires continuous adaptation and strategic positioning as industry boundaries continue to evolve. Organizations that effectively navigate this convergence will establish sustainable competitive advantages in the expanding digital economy.
The convergence of telecommunications and cloud computing represents a fundamental transformation that creates new opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and service delivery. This evolution requires strategic vision, substantial investment, and collaborative partnerships to realize its full potential. Organizations that successfully embrace this convergence position themselves advantageously for long-term growth and competitive success in an increasingly integrated digital landscape.